QBRI and Sultan Qaboos University Collaborate on Autism Spectrum Disorder Research
Study enhances understanding of the genetic factors implicated in ASD among Omani children, allowing for comparison with data from Qatar
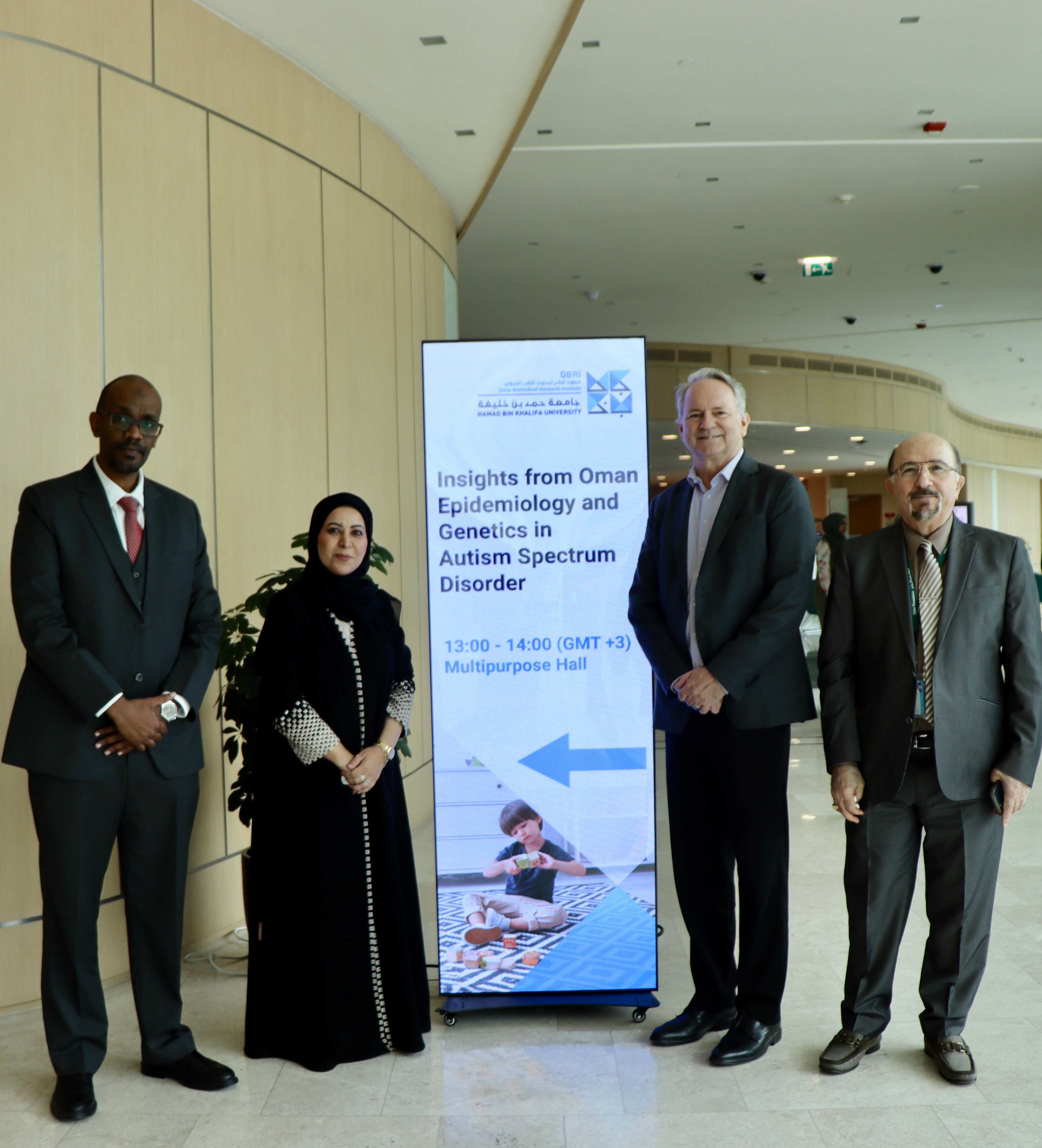

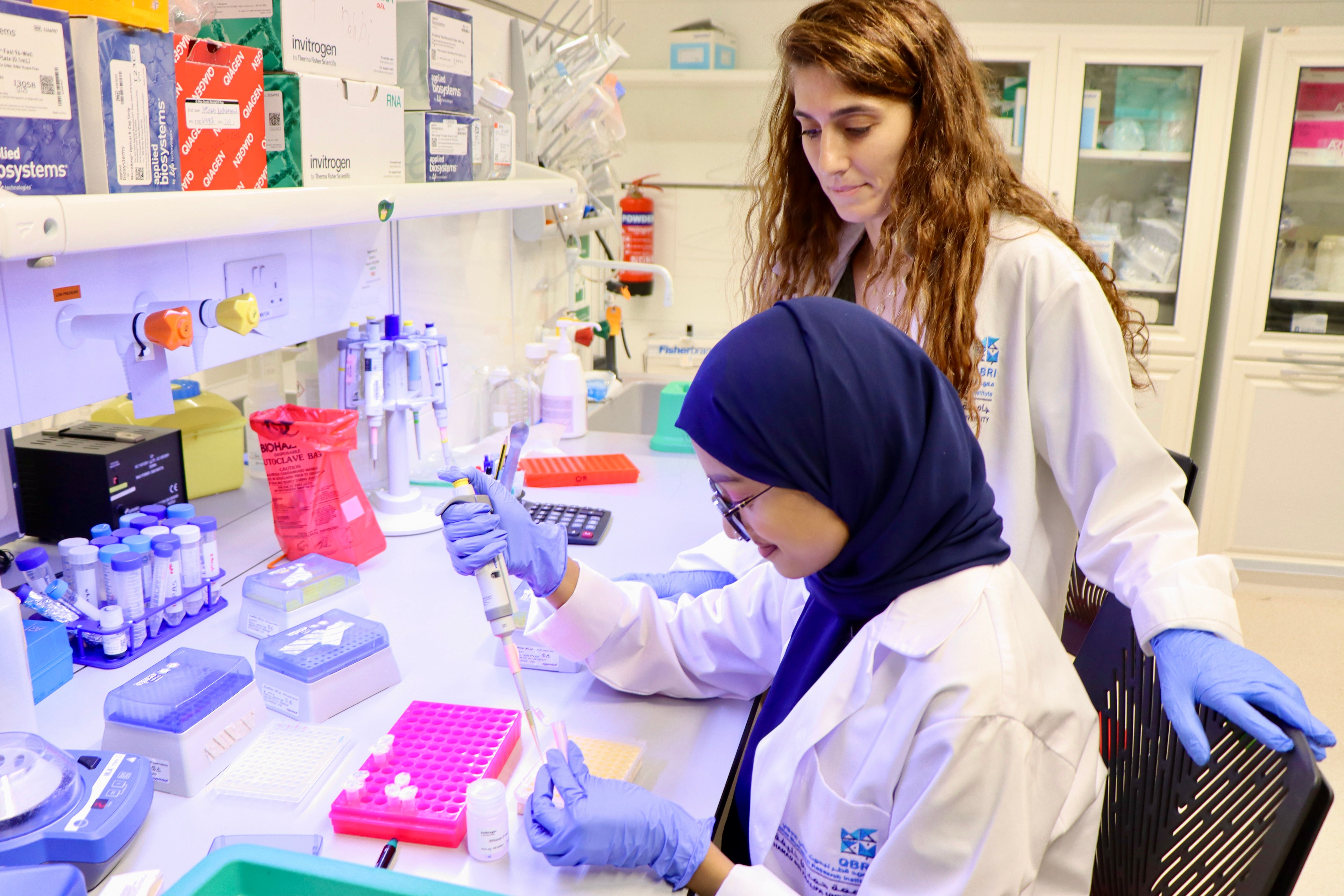
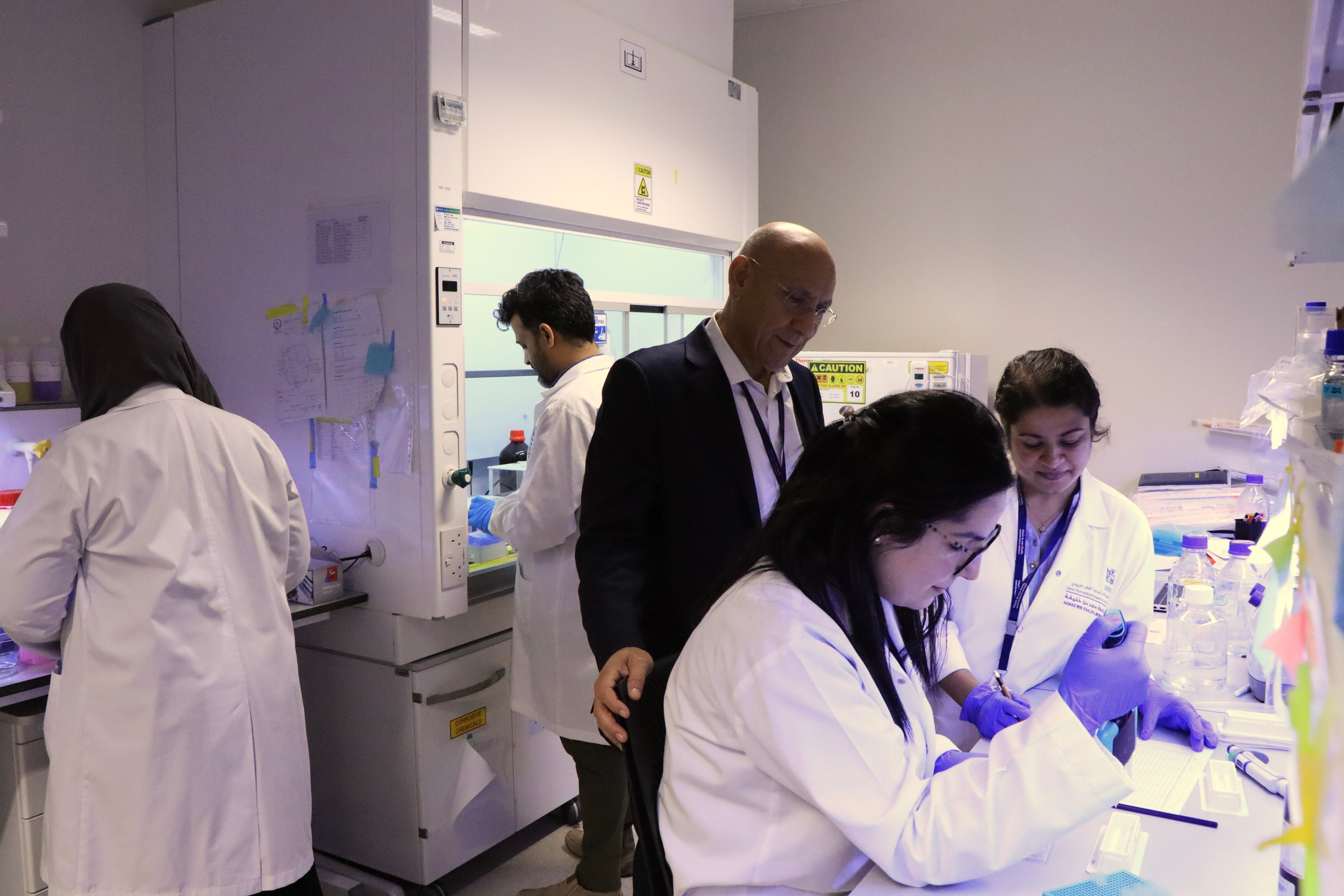
The Neurological Disorder Research Center (NDRC) at Hamad Bin Khalifa University’s (HBKU) Qatar Biomedical Research Institute (QBRI) and Oman’s Sultan Qaboos University (SQU) have embarked on a comprehensive joint study on genetic factors involved in autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
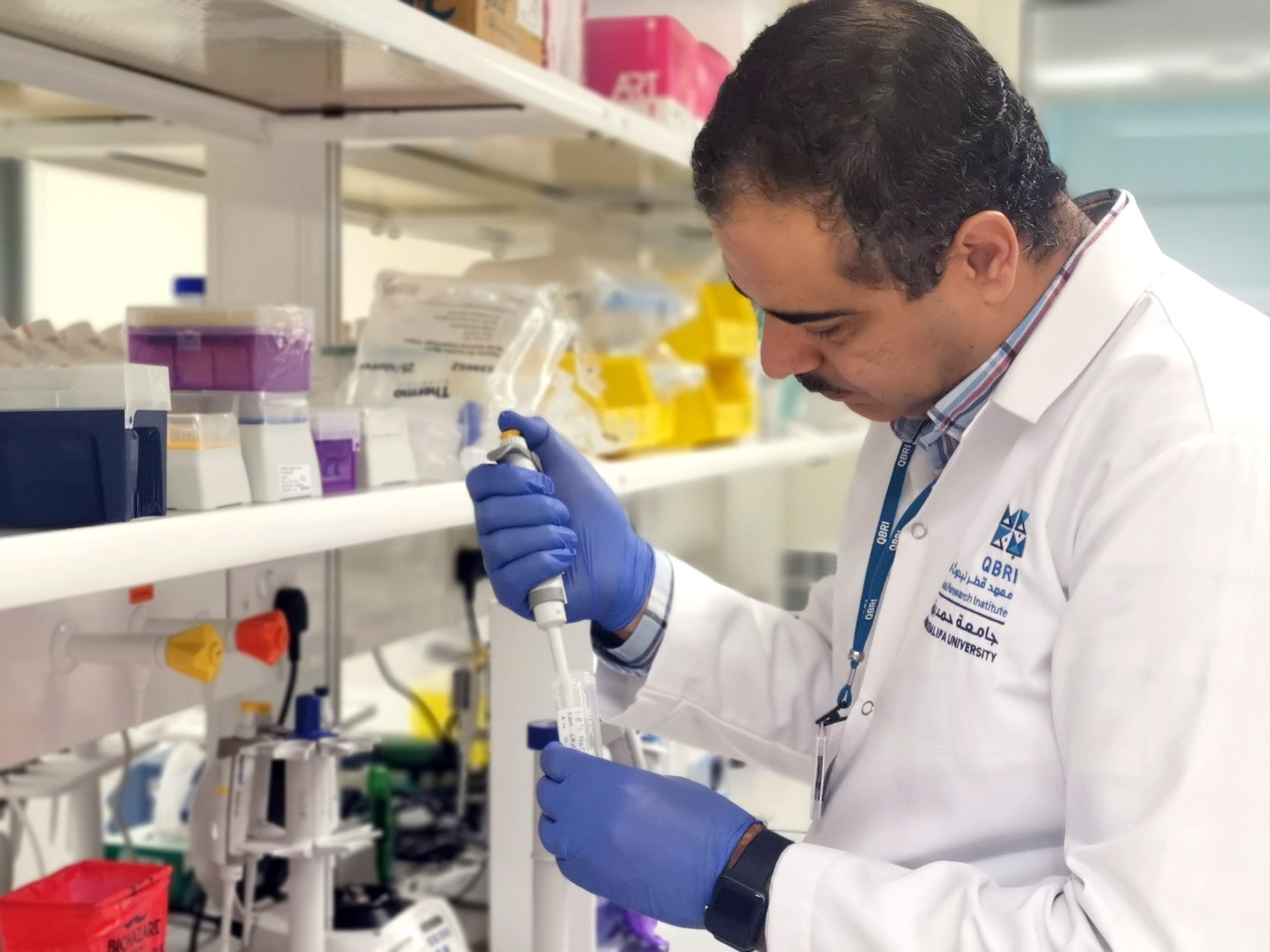
The collaboration is deciphering more than 100 rare genetic variants among a cohort of Omani children diagnosed with ASD. Furthermore, the team is determining the pathogenicity of these variants and studying their impacts in Autism Spectrum Disorder. SQU provided DNA to QBRI from the cohort consisting of 104 ASD families, each comprising both unaffected parents and the affected child. This structure facilitates the identification of rare genetic variants in the child with ASD or rare genetic variants that could pass down from their parents. Blood samples are collected from all family members, and genomic DNA is isolated. This genomic DNA, containing the complete genetic information, undergoes whole genome sequencing in Qatar to unveil genetic insights. This analysis is shedding light on the specific genetic factors contributing to ASD within the MENA population.
Led by Dr. Lawrence Stanton, Director of the NDRC, Dr. Vijay Gupta, Postdoctoral Researcher, and Dr. Afif Ben Mahmoud, Senior Research Associate, both from QBRI, and Dr. Watfa Al-Mamari, Senior Consultant, and Dr. Ahmed Idris, Consultant, both from SQU Hospital, the project is investigating the significance of these findings. The collaborative teams are also leveraging advanced genomic technologies and artificial intelligence to build a comprehensive database that combines results from the Omani cohort and data from a Qatari cohort of children diagnosed with ASD. This comparative approach seeks to discern similarities and differences in genetic variants between both populations.
Dr. Watfa concluded:“The study involves a comparative analysis between the genetic data obtained from the Omani cohort and existing data on clinical phenotypes and genetic etiologies collected from the Qatari ASD cohort. This comparative approach seeks to discern similarities or differences in genetic variants related to ASD between two populations.“
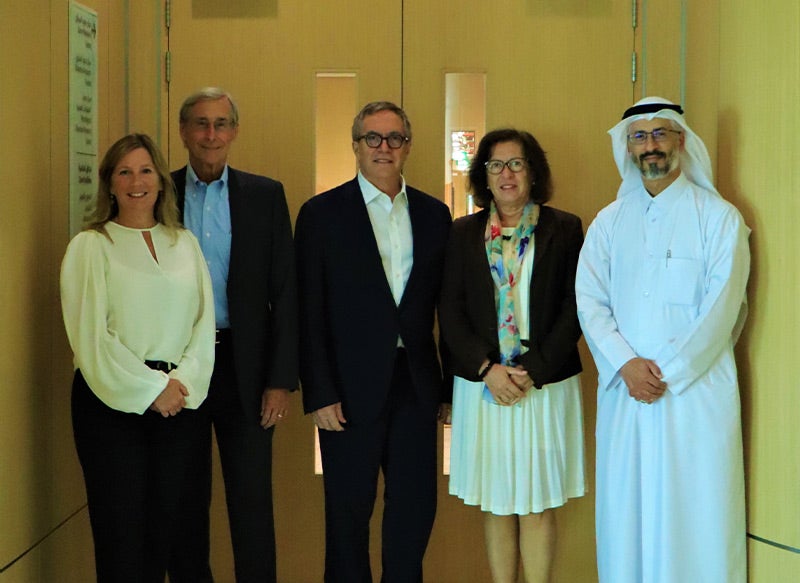
On April 30, 2024, Dr. Al-Mamari and Dr. Idris visited QBRI to further strengthen the collaborative efforts and discuss the project’s progress. During their visit, they presented an insightful seminar titled "Epidemiology and Genetics in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Insights from Oman," where they shared intriguing insights into the challenges and opportunities in ASD research within the Omani context.
Commenting on the importance of the project, Dr. Lawrence Stanton, QBRI, said: “While significant progress has been made in understanding ASD, there remains a crucial gap in comprehending the genetic factors contributing to the disorder, particularly within specific populations such as Oman. This collaborative endeavor aims to contribute to the global scientific understanding of the genetic basis of ASD, paving the way for improved care and support for individuals affected by ASD in Oman, Qatar, and beyond.”
Qatar Biomedical Research Institute (QBRI) is a leading research institute under Hamad Bin Khalifa University (HBKU). The institute addresses the Qatar National Health priorities outlined in the Qatar National Research Strategy through its dedicated research centers – the Translational Oncology Research Center, Diabetes Research Center (DRC) and Neurological Disorders Research Center (NDRC).
Related News

HBKU's QBRI Unveils Promising Arabic Stimuli: A Step Forward in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Diagnosis
Unveiling New Insights into Dementia: Autoantibodies and Blood-Based Biomarkers

Embracing the Colors of the Autism Spectrum: The Importance of Early Intervention and Advocacy
100-Year Anniversary of the Discovery of Insulin is of Great Relevance to QBRI

Qatar Biomedical Research Institute and Qatar University Scientists Conclude the International Symposium on Role of Glycation in Food-Health-Disease
QBRI Joins Hands with Qatar University to Provide Research Analytical Services
HBKU’s Qatar Biomedical Research Institute Continues to Bring Scientists Together Through Webinar Series

HBKU's QBRI Unveils Promising Arabic Stimuli: A Step Forward in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Diagnosis

Unveiling New Insights into Dementia: Autoantibodies and Blood-Based Biomarkers

Embracing the Colors of the Autism Spectrum: The Importance of Early Intervention and Advocacy

100-Year Anniversary of the Discovery of Insulin is of Great Relevance to QBRI

Qatar Biomedical Research Institute and Qatar University Scientists Conclude the International Symposium on Role of Glycation in Food-Health-Disease

QBRI Joins Hands with Qatar University to Provide Research Analytical Services

HBKU’s Qatar Biomedical Research Institute Continues to Bring Scientists Together Through Webinar Series

HBKU's QBRI Unveils Promising Arabic Stimuli: A Step Forward in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Diagnosis

Unveiling New Insights into Dementia: Autoantibodies and Blood-Based Biomarkers

Embracing the Colors of the Autism Spectrum: The Importance of Early Intervention and Advocacy

100-Year Anniversary of the Discovery of Insulin is of Great Relevance to QBRI

Qatar Biomedical Research Institute and Qatar University Scientists Conclude the International Symposium on Role of Glycation in Food-Health-Disease

QBRI Joins Hands with Qatar University to Provide Research Analytical Services

HBKU’s Qatar Biomedical Research Institute Continues to Bring Scientists Together Through Webinar Series

HBKU's QBRI Unveils Promising Arabic Stimuli: A Step Forward in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Diagnosis

Unveiling New Insights into Dementia: Autoantibodies and Blood-Based Biomarkers

Embracing the Colors of the Autism Spectrum: The Importance of Early Intervention and Advocacy

100-Year Anniversary of the Discovery of Insulin is of Great Relevance to QBRI

Qatar Biomedical Research Institute and Qatar University Scientists Conclude the International Symposium on Role of Glycation in Food-Health-Disease

QBRI Joins Hands with Qatar University to Provide Research Analytical Services

HBKU’s Qatar Biomedical Research Institute Continues to Bring Scientists Together Through Webinar Series

HBKU's QBRI Unveils Promising Arabic Stimuli: A Step Forward in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Diagnosis

Unveiling New Insights into Dementia: Autoantibodies and Blood-Based Biomarkers

Embracing the Colors of the Autism Spectrum: The Importance of Early Intervention and Advocacy

100-Year Anniversary of the Discovery of Insulin is of Great Relevance to QBRI

Qatar Biomedical Research Institute and Qatar University Scientists Conclude the International Symposium on Role of Glycation in Food-Health-Disease

QBRI Joins Hands with Qatar University to Provide Research Analytical Services

HBKU’s Qatar Biomedical Research Institute Continues to Bring Scientists Together Through Webinar Series

HBKU's QBRI Unveils Promising Arabic Stimuli: A Step Forward in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Diagnosis

Unveiling New Insights into Dementia: Autoantibodies and Blood-Based Biomarkers

Embracing the Colors of the Autism Spectrum: The Importance of Early Intervention and Advocacy

100-Year Anniversary of the Discovery of Insulin is of Great Relevance to QBRI

Qatar Biomedical Research Institute and Qatar University Scientists Conclude the International Symposium on Role of Glycation in Food-Health-Disease

QBRI Joins Hands with Qatar University to Provide Research Analytical Services

HBKU’s Qatar Biomedical Research Institute Continues to Bring Scientists Together Through Webinar Series

HBKU's QBRI Unveils Promising Arabic Stimuli: A Step Forward in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Diagnosis

Unveiling New Insights into Dementia: Autoantibodies and Blood-Based Biomarkers

Embracing the Colors of the Autism Spectrum: The Importance of Early Intervention and Advocacy

100-Year Anniversary of the Discovery of Insulin is of Great Relevance to QBRI

Qatar Biomedical Research Institute and Qatar University Scientists Conclude the International Symposium on Role of Glycation in Food-Health-Disease

QBRI Joins Hands with Qatar University to Provide Research Analytical Services

HBKU’s Qatar Biomedical Research Institute Continues to Bring Scientists Together Through Webinar Series

HBKU's QBRI Unveils Promising Arabic Stimuli: A Step Forward in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Diagnosis

Unveiling New Insights into Dementia: Autoantibodies and Blood-Based Biomarkers

Embracing the Colors of the Autism Spectrum: The Importance of Early Intervention and Advocacy

100-Year Anniversary of the Discovery of Insulin is of Great Relevance to QBRI

Qatar Biomedical Research Institute and Qatar University Scientists Conclude the International Symposium on Role of Glycation in Food-Health-Disease

QBRI Joins Hands with Qatar University to Provide Research Analytical Services

HBKU’s Qatar Biomedical Research Institute Continues to Bring Scientists Together Through Webinar Series

HBKU's QBRI Unveils Promising Arabic Stimuli: A Step Forward in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Diagnosis

Unveiling New Insights into Dementia: Autoantibodies and Blood-Based Biomarkers

Embracing the Colors of the Autism Spectrum: The Importance of Early Intervention and Advocacy

100-Year Anniversary of the Discovery of Insulin is of Great Relevance to QBRI

Qatar Biomedical Research Institute and Qatar University Scientists Conclude the International Symposium on Role of Glycation in Food-Health-Disease

QBRI Joins Hands with Qatar University to Provide Research Analytical Services

HBKU’s Qatar Biomedical Research Institute Continues to Bring Scientists Together Through Webinar Series

HBKU's QBRI Unveils Promising Arabic Stimuli: A Step Forward in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Diagnosis

Unveiling New Insights into Dementia: Autoantibodies and Blood-Based Biomarkers

Embracing the Colors of the Autism Spectrum: The Importance of Early Intervention and Advocacy

100-Year Anniversary of the Discovery of Insulin is of Great Relevance to QBRI

Qatar Biomedical Research Institute and Qatar University Scientists Conclude the International Symposium on Role of Glycation in Food-Health-Disease

QBRI Joins Hands with Qatar University to Provide Research Analytical Services

HBKU’s Qatar Biomedical Research Institute Continues to Bring Scientists Together Through Webinar Series

HBKU's QBRI Unveils Promising Arabic Stimuli: A Step Forward in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Diagnosis

Unveiling New Insights into Dementia: Autoantibodies and Blood-Based Biomarkers

Embracing the Colors of the Autism Spectrum: The Importance of Early Intervention and Advocacy

100-Year Anniversary of the Discovery of Insulin is of Great Relevance to QBRI

Qatar Biomedical Research Institute and Qatar University Scientists Conclude the International Symposium on Role of Glycation in Food-Health-Disease

QBRI Joins Hands with Qatar University to Provide Research Analytical Services

HBKU’s Qatar Biomedical Research Institute Continues to Bring Scientists Together Through Webinar Series

HBKU's QBRI Unveils Promising Arabic Stimuli: A Step Forward in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Diagnosis

Unveiling New Insights into Dementia: Autoantibodies and Blood-Based Biomarkers

Embracing the Colors of the Autism Spectrum: The Importance of Early Intervention and Advocacy

100-Year Anniversary of the Discovery of Insulin is of Great Relevance to QBRI

Qatar Biomedical Research Institute and Qatar University Scientists Conclude the International Symposium on Role of Glycation in Food-Health-Disease

QBRI Joins Hands with Qatar University to Provide Research Analytical Services

HBKU’s Qatar Biomedical Research Institute Continues to Bring Scientists Together Through Webinar Series

HBKU's QBRI Unveils Promising Arabic Stimuli: A Step Forward in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Diagnosis

Unveiling New Insights into Dementia: Autoantibodies and Blood-Based Biomarkers

Embracing the Colors of the Autism Spectrum: The Importance of Early Intervention and Advocacy

100-Year Anniversary of the Discovery of Insulin is of Great Relevance to QBRI

Qatar Biomedical Research Institute and Qatar University Scientists Conclude the International Symposium on Role of Glycation in Food-Health-Disease

QBRI Joins Hands with Qatar University to Provide Research Analytical Services

HBKU’s Qatar Biomedical Research Institute Continues to Bring Scientists Together Through Webinar Series

HBKU's QBRI Unveils Promising Arabic Stimuli: A Step Forward in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Diagnosis

Unveiling New Insights into Dementia: Autoantibodies and Blood-Based Biomarkers

Embracing the Colors of the Autism Spectrum: The Importance of Early Intervention and Advocacy

100-Year Anniversary of the Discovery of Insulin is of Great Relevance to QBRI

Qatar Biomedical Research Institute and Qatar University Scientists Conclude the International Symposium on Role of Glycation in Food-Health-Disease

QBRI Joins Hands with Qatar University to Provide Research Analytical Services

HBKU’s Qatar Biomedical Research Institute Continues to Bring Scientists Together Through Webinar Series

HBKU's QBRI Unveils Promising Arabic Stimuli: A Step Forward in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Diagnosis

Unveiling New Insights into Dementia: Autoantibodies and Blood-Based Biomarkers

Embracing the Colors of the Autism Spectrum: The Importance of Early Intervention and Advocacy

100-Year Anniversary of the Discovery of Insulin is of Great Relevance to QBRI

Qatar Biomedical Research Institute and Qatar University Scientists Conclude the International Symposium on Role of Glycation in Food-Health-Disease

QBRI Joins Hands with Qatar University to Provide Research Analytical Services

HBKU’s Qatar Biomedical Research Institute Continues to Bring Scientists Together Through Webinar Series

HBKU's QBRI Unveils Promising Arabic Stimuli: A Step Forward in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Diagnosis

Unveiling New Insights into Dementia: Autoantibodies and Blood-Based Biomarkers

Embracing the Colors of the Autism Spectrum: The Importance of Early Intervention and Advocacy

100-Year Anniversary of the Discovery of Insulin is of Great Relevance to QBRI

Qatar Biomedical Research Institute and Qatar University Scientists Conclude the International Symposium on Role of Glycation in Food-Health-Disease

QBRI Joins Hands with Qatar University to Provide Research Analytical Services

HBKU’s Qatar Biomedical Research Institute Continues to Bring Scientists Together Through Webinar Series

HBKU's QBRI Unveils Promising Arabic Stimuli: A Step Forward in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Diagnosis

Unveiling New Insights into Dementia: Autoantibodies and Blood-Based Biomarkers

Embracing the Colors of the Autism Spectrum: The Importance of Early Intervention and Advocacy

100-Year Anniversary of the Discovery of Insulin is of Great Relevance to QBRI

Qatar Biomedical Research Institute and Qatar University Scientists Conclude the International Symposium on Role of Glycation in Food-Health-Disease

QBRI Joins Hands with Qatar University to Provide Research Analytical Services

HBKU’s Qatar Biomedical Research Institute Continues to Bring Scientists Together Through Webinar Series

HBKU's QBRI Unveils Promising Arabic Stimuli: A Step Forward in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Diagnosis

Unveiling New Insights into Dementia: Autoantibodies and Blood-Based Biomarkers

Embracing the Colors of the Autism Spectrum: The Importance of Early Intervention and Advocacy

100-Year Anniversary of the Discovery of Insulin is of Great Relevance to QBRI

Qatar Biomedical Research Institute and Qatar University Scientists Conclude the International Symposium on Role of Glycation in Food-Health-Disease

QBRI Joins Hands with Qatar University to Provide Research Analytical Services

HBKU’s Qatar Biomedical Research Institute Continues to Bring Scientists Together Through Webinar Series

HBKU's QBRI Unveils Promising Arabic Stimuli: A Step Forward in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Diagnosis

Unveiling New Insights into Dementia: Autoantibodies and Blood-Based Biomarkers

Embracing the Colors of the Autism Spectrum: The Importance of Early Intervention and Advocacy

100-Year Anniversary of the Discovery of Insulin is of Great Relevance to QBRI

Qatar Biomedical Research Institute and Qatar University Scientists Conclude the International Symposium on Role of Glycation in Food-Health-Disease

QBRI Joins Hands with Qatar University to Provide Research Analytical Services

HBKU’s Qatar Biomedical Research Institute Continues to Bring Scientists Together Through Webinar Series

HBKU's QBRI Unveils Promising Arabic Stimuli: A Step Forward in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Diagnosis

Unveiling New Insights into Dementia: Autoantibodies and Blood-Based Biomarkers

Embracing the Colors of the Autism Spectrum: The Importance of Early Intervention and Advocacy

100-Year Anniversary of the Discovery of Insulin is of Great Relevance to QBRI

Qatar Biomedical Research Institute and Qatar University Scientists Conclude the International Symposium on Role of Glycation in Food-Health-Disease

QBRI Joins Hands with Qatar University to Provide Research Analytical Services