

في هذا الحوار، يناقش الدكتور ديفيد يانج، الأستاذ المشارك في كلية العلوم والهندسة، آفاق الذكاء الاصطناعي التحاوري وتطبيقاته الواسعة

الذكاء الاصطناعي التحاوري هو نوع من الذكاء الاصطناعي يسمح للحاسوبات والأجهزة الذكية بفهم اللغة البشرية والاستجابة لها. ويُستخدم هذا النوع من الذكاء الاصطناعي في روبوتات الدردشة وأدوات المساعدة الرقمية والتطبيقات الأخرى التي تعتمد على معالجة اللغات الطبيعية.
In this interview, Dr. David Yang, Associate Professor at CSE, discusses the prospects of conversational artificial intelligence and its industry-wide applications.

Conversational AI is a type of AI that allows computers and devices to understand and respond to human language. This type of AI is used in chatbots, digital assistants, and other applications that rely on natural language processing.
الدكتور أنطونيو بي سانفيليبو، كبير العلماء بمعهد قطر لبحوث البيئة والطاقة؛ وجيوفاني سكابيا، باحث مشارك في المعهد
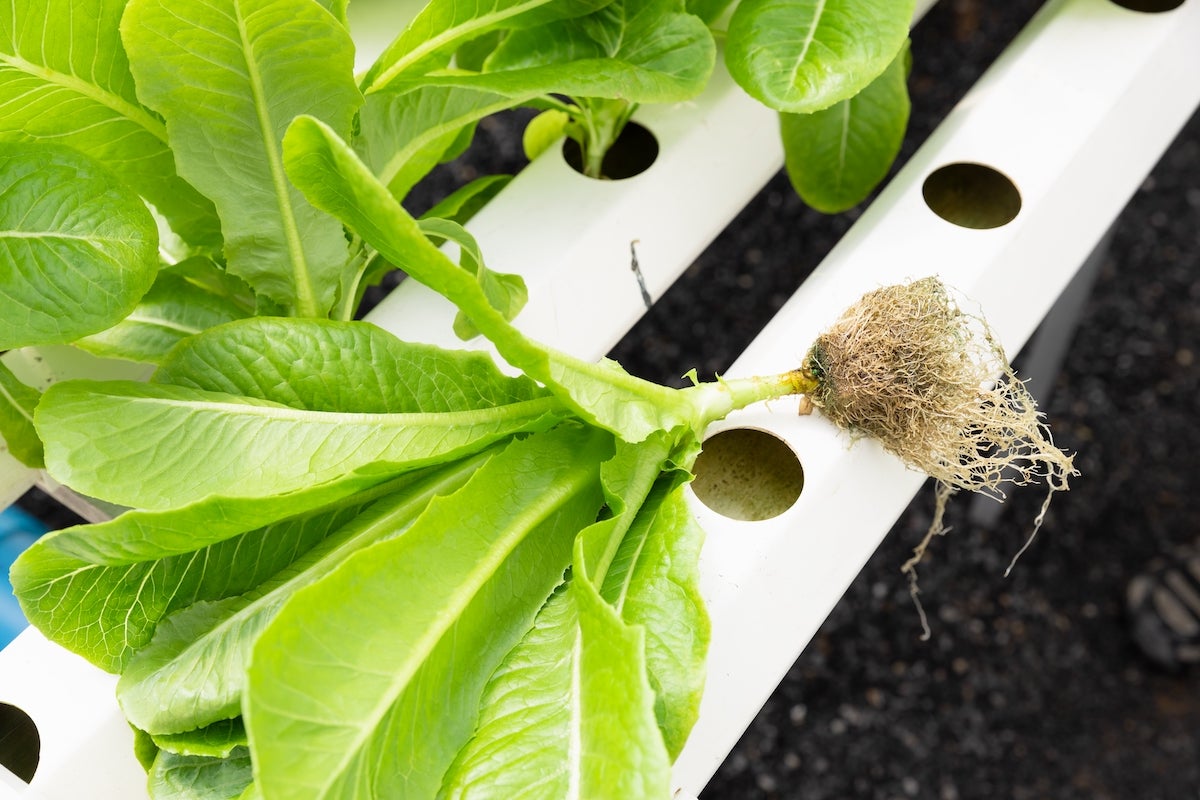

يتطلب تحقيق الاكتفاء الذاتي من الغذاء القيام بالأنشطة الزراعية على مدار السنة. ويعد هذا المسعى صعب التحقق في دولة قطر بسبب الظروف الجوية القاسية وندرة الأراضي الصالحة للزراعة وشُح الموارد المائية. لكنّ استخدام تقنيات الزراعة الداخلية كالزراعة المائية، يساعد على تجاوز نقص الأراضي الصالحة للزراعة ويوفر أحد أكثر الحلول كفاءة في استخدام المياه لإنتاج المحاصيل. ومع ذلك، فإن الزراعة الداخلية في درجات الحرارة المرتفعة - خاصة بين أبريل وأكتوبر- تتطلب استخدامًا كبيرًا للمياه من أجل التبريد بالإضافة إلى الري.
by Dr. Antonio P. Sanfilippo, Chief scientist, QEERI; and Giovanni Scabbia, Research Associate, QEERI

Achieving food self-sufficiency requires farming activities to take place all year-round. This is a challenging endeavor in Qatar due to the extreme weather conditions and the scarcity of arable land and water resources. The use of indoor farming practices such as hydroponics can address the lack of arable land and provide one of the most water-efficient solutions for producing crops. However, indoor farming in high temperatures - particularly between April and October - requires extensive use of water for cooling in addition to irrigation.
تحالف الطاقة الشمسية بمعهد قطر لبحوث البيئة والطاقة يطوِّر تقنيات الطاقة الشمسية لتناسب الظروف الصحراوية
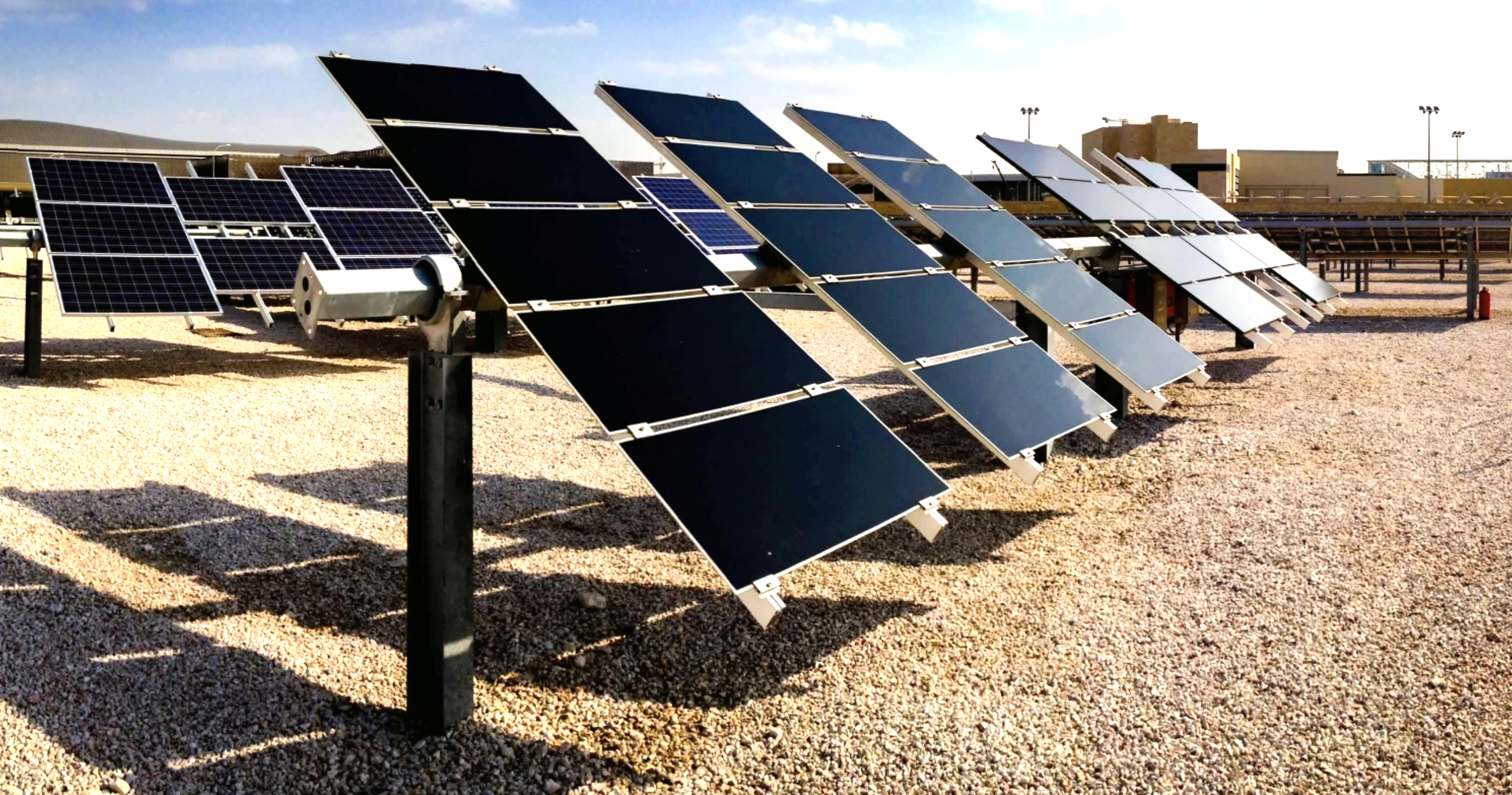

بدأ معهد قطر لبحوث البيئة والطاقة في جامعة حمد بن خليفة تشغيل نظام تعقب كهروضوئي جديد أفقي وأحادي المحور قادر على توفير بيانات حقيقية لزيادة إنتاجية الطاقة الشمسية في المناخات الصحراوية الحارة. يأتي المشروع في إطار مبادرة من تحالف الطاقة الشمسية بمعهد قطر لبحوث البيئة والطاقة، وهي مجموعة بحثية تضم المعهد وكهرماء وشركات تعمل في مجال الطاقة الشمسية من جميع أنحاء العالم.
QEERI Solar Consortium advances goal of developing solar technologies for desert conditions

Qatar Environment and Energy Research Institute (QEERI), part of Hamad Bin Khalifa University (HBKU), has begun operating a new horizontal single-axis photovoltaic (PV) tracker (HSAT) system capable of providing real-world data to maximizing solar energy generation in order to provide real-world data related to hot desert climates.
Dr. Anis Ben Brik, Associate Professor and Founding Director of the Program for Social Policy Evaluation and Research (PROSPER) at the College of Public Policy (CPP), participated in the recent Arab League Educational, Cultural and Scientific Organization (ALECSO) Scientific Chair for Sustainable Development Conference.