FIFA World Cup Fans Learn More about Future Impact of AI on Jobs and Employment
by Dr. Ghanim Mohammed Y J Al-Sulaiti
The world’s biggest sporting event, the FIFA World Cup 2022, created huge interest as Qatar reveled in becoming the first Arab nation to host the spectacle, which is held every four years.
With 32 participating national teams, Qatar hosted more than 1.2 million international visitors for more than a month. Fans who attended the matches at the eight world class stadia had the unique opportunity to experience the nearby Last-mile Cultural Activation, which featured thousands of arts, fashion, and design events, alongside blockbuster musical performances and film screenings.
Away from the stadia, in a family friendly environment, fans enjoyed live coverage of matches, stage performances, Qatari culture and a taste of local cuisines, and other cultural activities. These included the FIFA Fan Festival at Al Bidda Park, Al Maha Island in Lusail, the Arcadia Spectacular dance festival near Ras Bu Fontas, the 974 Beach Club, the Katara Cultural Village, Msheireb Downtown Doha, and Souq Waqif. One of the hottest spots during the World Cup was the Corniche, which had a carnival atmosphere spreading 6km from the Sheraton Hotel to the Museum of Islamic Art.
Featuring the global goals
In an exciting collaboration, Qatar Computing Research Institute (QCRI), part of Hamad Bin Khalifa University (HBKU), teamed up with Silatech, to raise awareness about the potential impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on jobs.
Silatech, an international nonprofit and nongovernmental development organization aiming to achieve the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through the economic empowerment of youth, hosted a range of events on the Corniche, in collaboration with different organizations. The events drewing attention to the UN’s SDG 8, which promotes inclusive and sustainable economic growth, employment, and decent work for all. Through its digital walk through exhibition, Silatech showcased the situation in refugee camps across the globe and promoted different aspects of youth employment.
Looking closely at AI technology
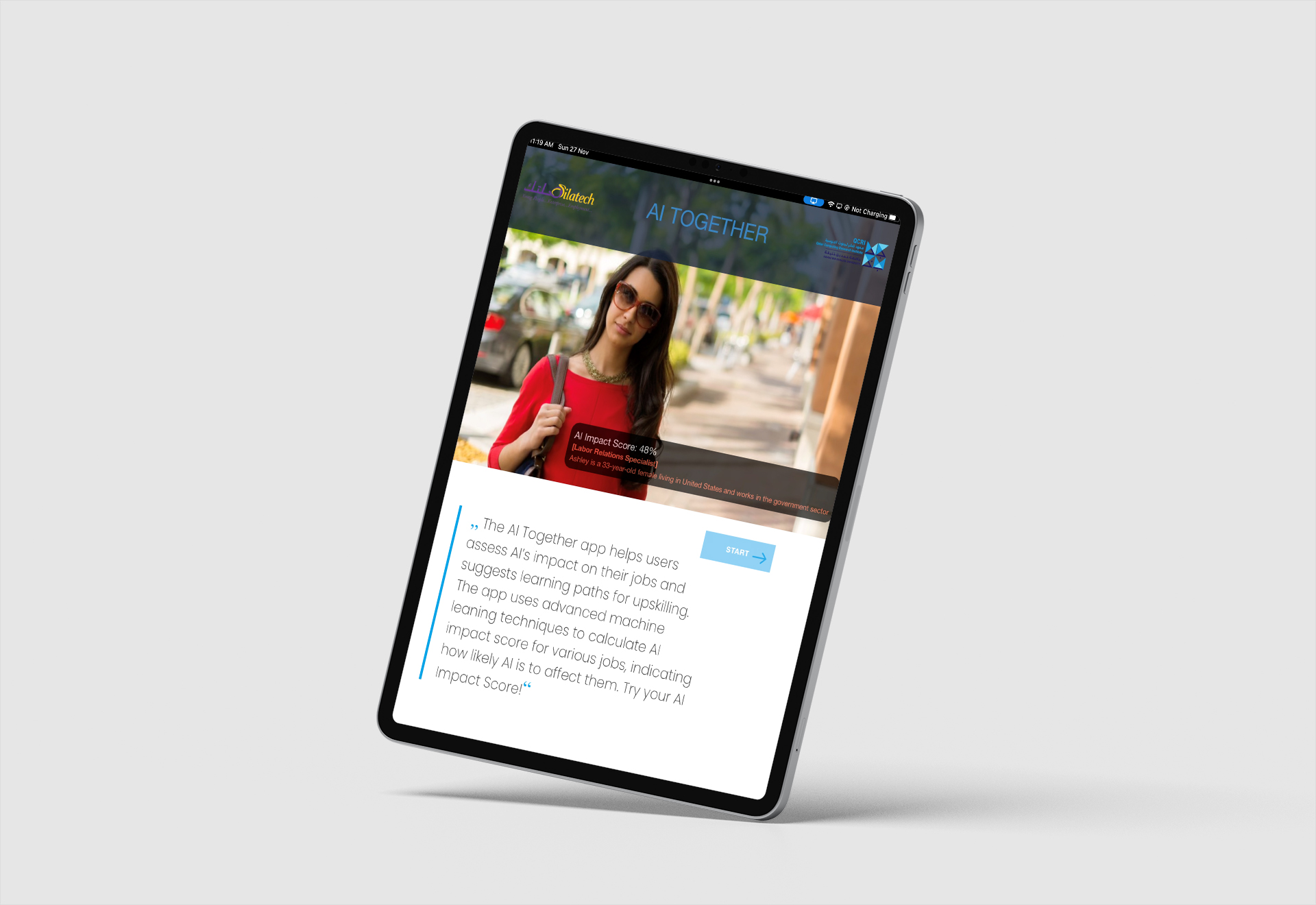
QCRI previously developed an AI system that determines the susceptibility of different jobs to AI technology (e.g., how AI can improve the efficiency and productivity of task performance within a job). The system achieves this by computing an impact score using two different kinds of inputs: (1) patents on AI; and (2) job descriptions. It processes more than 1.5 million patents acquired from the Google patents database, in addition to more than 1,000 job descriptions, acquired from the Occupational Information Network (O*Net) database managed by the US Department of Labor. The job descriptions contain overviews and the tasks inherent to each job. The AI system uses advanced machine-learning techniques to match the jobs and their tasks with relevant AI patents. The more matched patents for a job, the more likely the job is to be impacted by AI.
Unlike earlier industrial revolutions that impacted blue-collar jobs, AI is mostly impacting white-collar jobs. In particular, AI impacts jobs with cognitive non-routine tasks such as memorization, information ordering, visualization, deductive reasoning, and speech recognition. Hence, AI is mostly impacting white-collar jobs that usually require formal education. These jobs include business professionals, law professionals, social workers, managers, health professionals, sales workers, and clerks. On the other hand, jobs that focus on physical tasks, like cleaners and helpers, fishers, farmers and chefs, are the least impacted by AI.
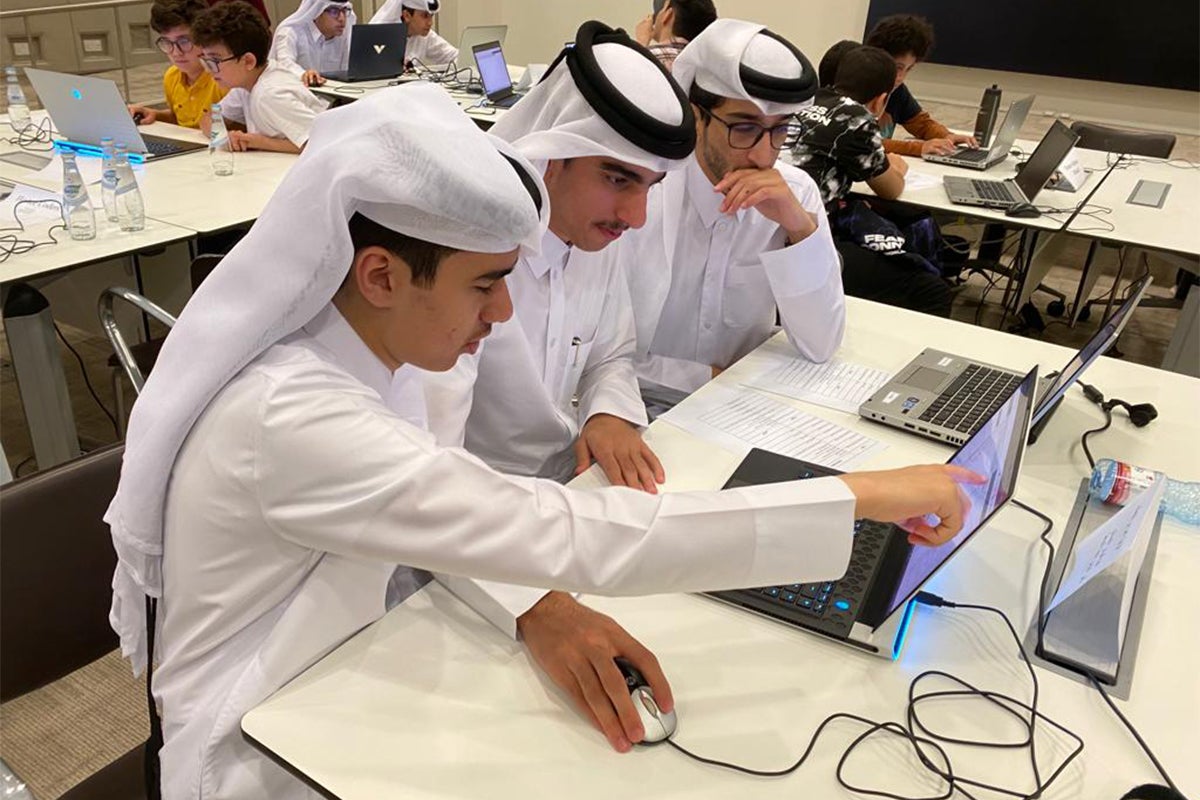
For the World Cup, QCRI customized the system for use on iPads and made it interactive, educational, and - most importantly - fun. Attendees at the digital exhibition interacted with the system through different iPad stations. Users were able to select their jobs, determine the tasks relevant to the job, guess the impact score for each task, and view the real impact score based on the data processed by the system.
Ji Lucas, Senior Software Engineer at QCRI, explained: “We had initially developed the system to complement the white paper on the impact of AI on jobs in Qatar. When we were approached by Silatech and offered the opportunity to participate in the SDG 8 event, we had to create a game-like scenario so that World Cup fans could have a fun time with the app and learn more about the impact of AI on their jobs.”
Besides the AI system, visitors could learn more about the impact of AI on the different skill sets required in the future through the exhibition, which showcases QCRI’s research in this area on different digital screens.
Having exposure to such information helps the youth to make better-informed decisions about their careers and have a better idea about the type of skills they should nurture in order to adapt to the future implication of AI on jobs.
“We are glad to collaborate with Silatech and have this opportunity to make a positive impact during the World Cup. Having spearheaded work on AI and its effect on the workforce in Qatar, we were excited to share our knowledge with World Cup fans on the different implications of AI on jobs,” said Dr. Ahmed K. Elmagarmid, the founding Executive Director of QCRI.
Dr. Ghanim Mohammed Y J Al-Sulaiti is a Scientist at Qatar Computing Research Institute, Hamad Bin Khalifa University.
Related News

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction

QCRI and UNDP to Host Workshop on Artificial Intelligence as Tool for Social Good

Middle School Seniors Become Technology Creators at Qatar Computing Research Institute’s Creative Space Summer Camp

New Study by HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute and Sidra Medicine Reveals Genetic Influence on Cancer Immune Responsiveness

HBKU’s Qatar Computing Research Institute Studies Impact of Fasting on Diabetic Patients

HBKU Preparing to Stage First International Conference on Visualization and Computer-Human Interaction













